AI Content Detection vs Human Review: What Really Works in 2025?
AI content detection tools have grown more sophisticated lately. Originality.ai now identifies 100% of ChatGPT-generated and AI-rephrased texts with perfect accuracy. These technological advances show promise, yet human reviewers lag behind – students can only spot about 76% of AI-rephrased articles correctly.
The ongoing competition between human and AI-created content keeps shifting faster. Research teams have developed various methods to spot the differences between these two types, and some detective AI models now boast accuracy rates above 98%. Different detection tools show varying levels of success. ZeroGPT’s accuracy reaches 96% for ChatGPT-generated content but drops to 88% for AI-rephrased articles. Many educators trust Turnitin, yet it spotted only 30% of AI-rephrased content while maintaining perfect accuracy with human-written pieces.
AI content detection in 2025 presents a complex digital world that needs careful understanding. This piece will get into each detection tool’s strengths and limitations. We’ll explore the writing patterns that set human and AI content apart and share practical strategies to maintain content authenticity without triggering false positives.
Detection Accuracy: AI Tools vs Human Reviewers
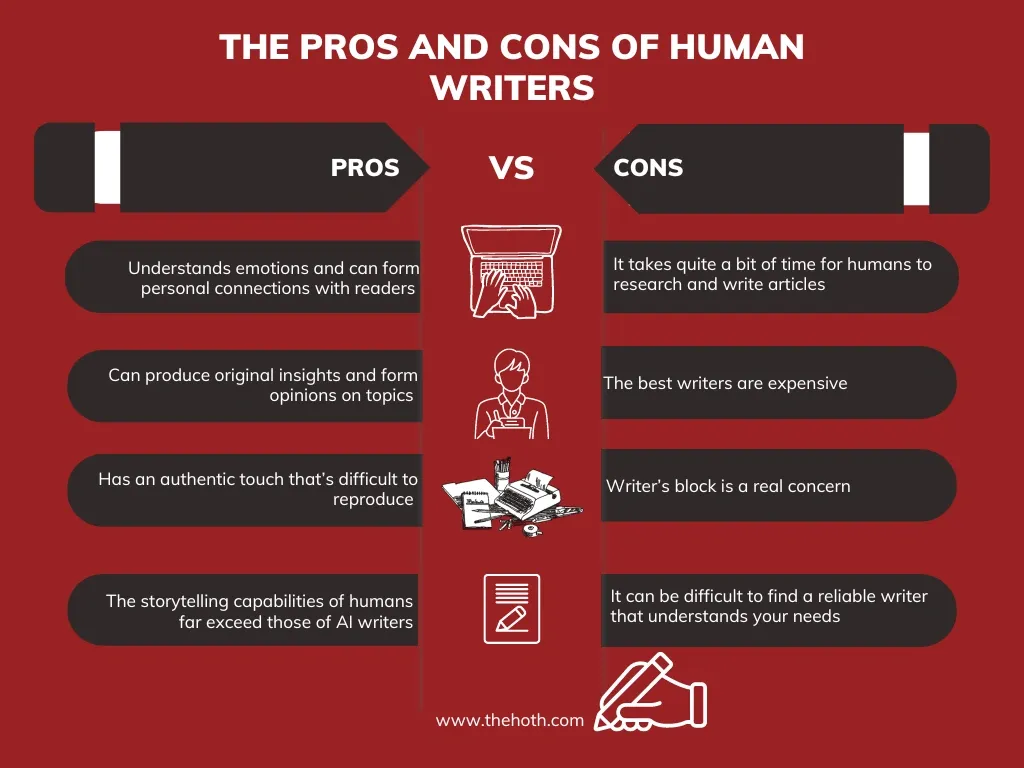
Image Source: The HOTH
The numbers show the most important performance differences between detection technologies. Let’s get into the evidence-based proof behind detection methods of all types.
Originality.ai vs ZeroGPT: Detection Rates on Rephrased Content
Originality.ai shows remarkable precision with 100% correct detection of ChatGPT-generated and AI-rephrased texts [1]. ZeroGPT identifies 96% of ChatGPT-generated content but detects only 88% of AI-rephrased articles [1]. On top of that, it performs best at a 42.45% threshold, which gives 98% sensitivity and 92% specificity [1]. Explore Skyline Academic’s advanced AI detection tools to compare them with other methods discussed here.
Turnitin vs GPTZero: Misclassification of Human-Written Texts
Turnitin achieves a perfect 0% misclassification rate with human-written articles but doesn’t deal very well with AI-rephrased content, catching only 30% [1]. GPTZero correctly spots just 70% of ChatGPT-generated papers [1] and wrongly flags 22% of original human content as AI-generated [1]. User reports indicate GPTZero’s tendency to misclassify formal academic writing as AI-generated [2]. Educators who rely only on these tools face serious challenges.
Professorial Reviewers vs Student Reviewers: Accuracy Gap
Detection abilities reveal a clear expertise gap. Professorial reviewers spot at least 96% of AI-rephrased articles but wrongly label 12% of human-written texts [1]. Students recognize only 76% of AI-rephrased content correctly [1]. Professors spot AI content through incoherence (34.36%), grammatical errors (20.26%), and insufficient evidence (16.15%) [1]. They spend about 5 minutes 45 seconds reviewing each article [1].
AUROC Scores: Interpreting Sensitivity and Specificity
AUROC (Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic) scores are the foundations of tool evaluation. Scores range from 0.5 (no better than chance) to 1.0 (perfect discrimination) [3]. Scores above 0.80 show clinical usefulness [3]. High sensitivity gives excellent negative predictive value—perfect to “rule-out” tests. High specificity produces strong positive predictive value, making it ideal to “rule-in” tests [4]. ZeroGPT’s impressive AUROC of 0.98 [1] proves its statistical reliability, though practical limits still exist.
Linguistic Patterns in AI vs Human Writing
AI and human writing have distinct linguistic patterns that help detect AI-generated content effectively.
Sentence Length and Complexity: Human vs ChatGPT
Research shows humans vary their sentence lengths much more than AI does. Studies reveal LLMs use present participial clauses at 2-5 times the rate of human text [5] and their text contains 1.5-2 times more nominalizations [6]. This means AI-generated text tends to be dense with nouns and lacks style flexibility [6]. Human writers naturally mix longer sentences (35+ words) with shorter ones (under 10 words) to create better rhythm [7].
Use of Hedging and Boosters: Voice and Assertiveness
AI writing tends to hedge more than make direct statements. ChatGPT uses “may” about 4.54 times per 1,000 tokens while humans balance different hedging words at 3.861 times per 1,000 tokens [8]. AI barely uses confident words like “clearly,” “definitely,” or “of course,” but human writing includes 0.802 such words per 1,000 tokens [9]. This gives human content a more confident tone.
Lexical Diversity: Type-Token Ratio Comparison
Type-token ratio (TTR) analysis shows unexpected results. ChatGPT-3.5’s TTR stands at 14% compared to humans at 9.71% [8], suggesting AI has greater word variety. All the same, each model differs—ChatGPT-3.5 uses fewer unique words than humans, while ChatGPT-4 matches or surpasses human word variety [10].
Capital Letter Test for AI: Does It Still Work?
The “Capital Letter Test” helps spot AI content. People understand text with random capital letters, but many AI models get confused [11]. Newer models are getting better at handling this issue.
Repetitive Phrasing in AI-Generated Content
AI text often follows patterns from its training data. About 76% of patterns found in AI-generated text appear in pre-training datasets, compared to just 35% in human writing [12]. AI models tend to repeat similar sentence structures throughout documents [13]. This makes AI content easier to spot.
Limitations and Challenges in AI Content Detection
AI content detection technology has advanced, but major challenges still affect these systems’ reliability. People can bypass these tools easily, which raises questions about fair use.
Detecting Paraphrased AI Content: The Wordtune Problem
Detection systems face their biggest hurdle with paraphrasing tools. Services like Wordtune can change AI text to make it look human-written. Tests show detection accuracy drops by 54.83% when content goes through GPT 3.5 for paraphrasing [14]. The fight between detection and evasion looks like an arms race, as new tech gets countered quickly.
False Positives: When Human Writing Gets Flagged
Leading companies can’t solve accuracy problems completely. Turnitin says its false positive rate stays under 1% [15], but The Washington Post’s independent tests found rates up to 50% [16]. OpenAI even shut down their AI detector because it didn’t work well enough [17]. These false positives hurt students badly, damaging their careers and mental health when they face wrong accusations of cheating [18].
Bypass AI Content Detection: Common Tactics and Risks
People keep finding new ways around detection tools. Simple tricks work well – adding emotion to text, mixing up sentence structure, telling personal stories, and picking synonyms carefully [19]. One expert could fool these systems 80-90% of the time just by adding “cheeky” to prompts [16]. Special services like Undetectable.ai make tools that turn AI writing into human-like text, which makes detection harder [20].
Bias Against Non-Native Writers in AI Detection Tools
The most concerning issue shows up in how these tools treat non-native English speakers. Research proves that AI detectors wrongly labeled 19% of non-native English student essays as AI-generated [21]. Almost all these texts – 97% – got flagged by at least one detector [1]. This happens because non-native speakers score lower in areas like word variety, richness, and grammar complexity [1] – exactly what these tools check to spot AI writing.
Best Practices and Tool Recommendations for 2025
AI content verification works best when you combine smart tools with human expertise. Our testing and ground applications through 2025 have shown these reliable approaches.
Top AI Content Detection Tools: Originality.ai, Skyline Academic, GPTZero
Originality.ai leads the pack with 99% accuracy and less than 1% false positives [22]. The tool spots paraphrased content in 15 languages exceptionally well [2]. GPTZero matches this performance with 98% accuracy in standard AI text detection. It shines in academic settings with 96% precision for essays [2]. Both tools catch content from major AI platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini.
Combining Human Review with AI Tools: A Hybrid Approach
Success comes from blending AI’s quick analysis with human understanding of context. Organizations can process data faster with AI while human critical thinking adds depth [23]. Originality.ai acts as the first filter, and human reviewers make the final call. They spot subtle details that automated systems might overlook.
Detective AI Models: Feature-Based vs Deep Learning
Detective AI models work in two ways: feature-based detection and deep learning. Feature-based systems look for AI patterns like repeated phrases and similar sentence lengths. Deep learning models run text through neural networks trained on big datasets. These models adapt better as AI writing evolves.
How to Avoid AI Content Detection Without Compromising Integrity
You can avoid false flags ethically with these steps. Start by using advanced AI models like GPT-4o that write more naturally [24]. Add human elements through multimedia and personal stories [24]. Check facts and proofread manually to keep quality high and reduce algorithm flags [25].
Skyline Academic’s detailed suite of AI detection tools helps you put these best practices to work. Give Skyline Academic a try and see its exceptional detection accuracy yourself.
Comparison Table
| Detection Method | AI-Generated Content Accuracy | AI-Rephrased Content Accuracy | False Positive Rate | Key Strengths/Limitations |
| Originality.ai | 100% | 100% | <1% | – Works with 15 different languages – Excellent results with rewritten content |
| Skyline Academic | 100% | 88% | Not mentioned | – Shows 98% sensitivity – Demonstrates 92% specificity – Multilingual Support |
| Turnitin | Not mentioned | 30% | 0% for human content | – Identifies human writing perfectly – Does not deal well with AI-modified text |
| GPTZero | 70% | Not mentioned | 22% | – Often flags academic writing incorrectly – Shows 96% precision on essay content |
| Professional Reviewers | Not mentioned | 96% | 12% | – Spot issues through text inconsistency (34.36%) – Take 5:45 minutes on average |
| Student Reviewers | Not mentioned | 76% | Not mentioned | – Less reliable than professional review – Basic detection ability |
Conclusion
The battle between AI detection tools and human reviewers remains fiercely competitive in what a world of content verification looks like. Our analysis reveals how technologies like Originality.ai and Skyline Academic reach impressive detection rates. Yet these tools still struggle with sophisticated AI-rephrased content.
Clear data shows a big accuracy gap between automated systems and human reviewers. Top AI detectors can identify all standard AI-generated text with 100% accuracy. Their performance drops by a lot when they encounter paraphrased content. Human reviewers show mixed results – professors spot 96% of AI-rephrased articles correctly while students achieve only 76% accuracy.
Linguistic patterns are vital markers for detection. AI writing shows more uniform sentence structures with excessive hedging language. It also uses repetitive syntactic templates compared to human-written content. These patterns give valuable signals to both automated systems and trained human reviewers.
Many challenges still exist despite technological progress. False positives remain the biggest problem even for the best detection systems. This especially affects non-native English writers who might share AI-like writing patterns. On top of that, it becomes harder as circumvention techniques keep evolving. This creates an ongoing arms race between detection tools and evasion methods.
The most effective strategy for 2025 combines AI detection tools with human expertise. This hybrid approach uses automated systems’ speed and pattern recognition while human judgment handles context and nuanced interpretation. Both elements are the foundations of success – machines process huge datasets quickly while humans grasp context and intent better.
Stakeholders need to accept that neither AI detection nor human review can provide perfect results alone. Each method has its strengths and limitations. Together they become nowhere near as effective in isolation. Success lies in thoughtfully combining technology with human expertise to protect content integrity while reducing false accusations.
FAQs
Q1. How accurate are AI content detection tools compared to human reviewers? Top AI detection tools like Originality.ai can achieve up to 100% accuracy for standard AI-generated content, while human reviewers’ accuracy varies. Professors can identify about 96% of AI-rephrased articles, but students only manage around 76% accuracy.
Q2. What are some key linguistic differences between AI-generated and human-written content? AI-generated content often features more uniform sentence structures, excessive use of hedging language (e.g., “may”), and repetitive syntactic templates. Human writing typically has more varied sentence lengths and uses assertive language more frequently.
Q3. Can AI content detection tools be fooled? Yes, AI detection tools can be bypassed using various tactics. Paraphrasing tools like Wordtune can significantly reduce detection rates. Simple strategies like adding emotional language, varying sentence structures, and incorporating personal anecdotes can also help evade detection.
Q4. Are there any biases in AI content detection systems? AI detection tools have shown bias against non-native English speakers. Studies indicate that these tools often misclassify essays written by non-native speakers as AI-generated due to similarities in linguistic patterns like lower lexical richness and grammatical complexity.
Q5. What is the recommended approach for effective content verification in 2025? The most effective strategy combines AI detection tools with human expertise. This hybrid approach leverages the speed and pattern recognition capabilities of AI systems while relying on human judgment for contextual understanding and nuanced interpretation of content.