AI Detectors vs Human Judgment: How Accurate Are They Really? [2025 Tests]
Are AI detectors reliable enough to spot machine-generated content? These tools have gained popularity lately, but they’re nowhere near perfect. Research shows AI detectors are “neither accurate nor reliable” and generate too many false positives and negatives. Turnitin claimed their AI checker had less than 1% false positive rate. A Washington Post study later proved this wrong, showing a staggering 50% false positive rate. OpenAI eventually discontinued their own AI detection software because it didn’t work well enough.
You might ask how these AI detectors work and why their accuracy varies so much. The tools look for specific text patterns to flag AI-generated content, but the results don’t stay consistent. Turnitin’s detection tool misses about 15% of AI-generated text in documents. Skyline Academic’s platform performs better. Their technology analyzed over 20,000 human-written papers and achieved a false positive rate of just 0.2% – making them the industry leader. This huge gap makes us question whether AI detectors can judge student work accurately.
How AI Detectors Work vs Human Evaluation
Image Source: ResearchGate
AI detectors use sophisticated algorithms to tell the difference between human and machine-generated text. We need to understand how automated tools and human evaluation work to figure out which method gives better results when spotting AI content.
Detection Mechanism: How Do AI Checkers Work?
AI detection tools use machine learning models that learn from large datasets of both human and AI-generated content [1]. These tools look at two key language features: perplexity and burstiness. Text predictability is measured through perplexity – AI content usually has lower scores because it follows common language patterns [2]. The variation in sentence structure and length shows up in burstiness scores, where AI writing typically shows less variety than human text [3].
Most detection systems use classifiers that put text into specific groups based on patterns they’ve learned. They give confidence scores that show how likely the text was written by AI [3]. While many tools claim they’re highly accurate, studies tell a different story. Research shows Originality.ai got 100% accuracy when detecting both ChatGPT-generated and AI-rephrased articles [4]. But another study found that even the best detection tools were only 85-95% accurate [5].
Human Judgment: Contextual Clues and Writing Style Recognition
Human reviewers check content by looking at tone, flow, fact consistency, and natural writing style changes [6]. They watch for warning signs like fact errors (AI hallucinations), predictable paragraph structures, and writing that lacks personality [7].
The surprising part is that humans aren’t always better at detection than machines. A study revealed that regular human evaluators spotted AI texts just slightly better than guessing – 57% for AI texts and 64% for human-written ones [8]. Professional reviewers did much better though. Two professors got impressive results with 96% and 100% accuracy when identifying AI-rephrased articles [4].
Speed and Scalability: AI vs Human Review Time
AI detectors work substantially faster than humans. These tools can check thousands of documents in seconds [9]. This makes them perfect for schools and companies that need to process lots of content. Human review takes much longer – a study found reviewers needed about 5 minutes and 45 seconds to check each article [4].
AI tools are fast and consistent, but they can’t match human intuition, cultural awareness, and ethical judgment [6]. The best solution for important work in education, journalism, or legal documents combines both methods. AI detection does the first screening, and humans check any flagged content carefully [6].
Accuracy in Real-World Scenarios
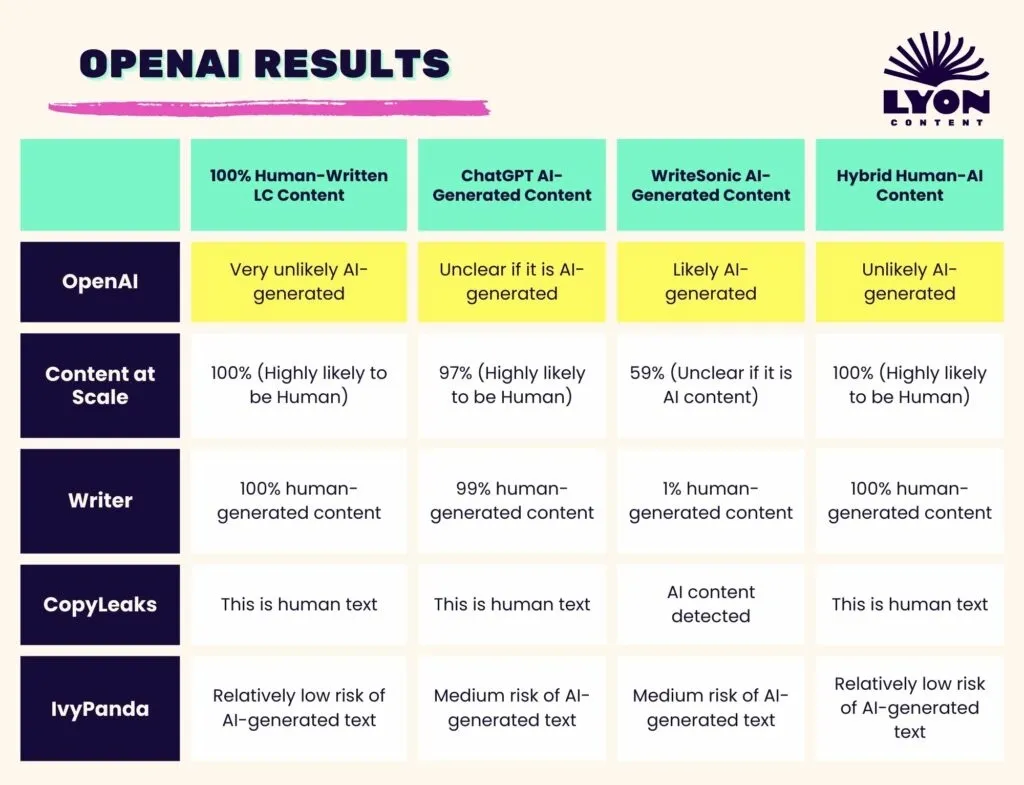
Image Source: Lyon Content Writing Agency
Testing shows troubling gaps between AI detection companies’ accuracy claims and their actual performance. These differences raise serious questions about how reliable these tools really are.
False Positives: Human Text Flagged as AI
Turnitin claims false positive rates below 1% [10]. However, studies reveal these rates can spike to 50% under certain conditions [11]. A mere 1% error rate means about 223,500 first-year college students’ essays get wrongly flagged each year [12]. Students face harsh penalties from these false accusations. They can lose scholarships and damage their relationships with faculty members permanently [12].
False Negatives: AI Text That Goes Undetected
Detection tools often miss AI-generated text, which becomes harder to spot with basic modifications. Users bypass these systems through paraphrasing, emotional content addition, or specialized tools like Writesonic’s AI Humanizer or UndetectableAI [11]. A legal expert points out that adding simple words like “cheeky” to prompts fools detection tools 80-90% of the time [11].
2025 Standard Tests: AI Detectors vs Educators
Tests show human evaluators struggle more than AI detectors. Teachers have a 5% false positive rate compared to detection tools’ 1.3% [13]. Stanford University researchers found professors couldn’t spot ChatGPT-generated texts among student essays reliably. Yet, these professors felt very confident about their judgment [14].
Bias in Detection: ESL and Neurodivergent Student Effect
Vulnerable student groups bear the heaviest burden. Stanford’s research shows AI detectors wrongly flag non-native English speakers‘ writing as AI-generated 61.2% of the time [15]. US-born students’ essays get more accurate evaluations. Neurodivergent students also face higher false-positive rates because their writing style might seem formulaic [16]. Skyline’s academic resources offer more detailed information about AI detection accuracy and educational integrity.
Ethical and Practical Implications
AI detection tools raise more than just accuracy concerns. These technologies create complex challenges that affect educational integrity and relationships between students and faculty.
Transparency Issues: The ‘Black Box’ Problem
AI detection tools work like “black boxes” and even their creators can’t explain the internal processes [17]. People see what goes in and what comes out but can’t verify how decisions happen. This creates a basic trust problem. The lack of transparency hides potential biases and weak points that might exist in these systems [1]. Modern AI detection models sacrifice clarity to gain power. This makes it sort of hard to get one’s arms around how these tools reach their conclusions.
Student Trust and Faculty Relationships
AI detectors have damaged trust between educators and students by a lot. Research shows that 62% of teachers report they don’t trust student work as much due to AI concerns [2]. Students feel watched instead of supported in this surveillance-focused environment [3]. False accusations damage emotions and block open communication—vital elements that help education work.
Legal and Academic Consequences of Misidentification
Wrong identifications lead to serious problems:
- Academic penalties including course failure and misconduct violations [18]
- ESL students and neurodivergent writers face bigger challenges [12]
- Schools face legal issues when they act based on incorrect detection [19]
Courts have started looking at AI-related issues in legal settings. They warn about possible penalties for AI-generated submissions that contain made-up information [20].
Head over to Skyline’s academic resources to learn more about handling ethical challenges of AI detection in education.
The Evolving Arms Race: AI Generators vs Detectors
The battle between AI generators and detectors gets more intense as both technologies evolve faster. This constant competition affects how schools deal with AI-generated content.
Detection Evasion Tools: Writesonic, Undetectable AI
New tools help users dodge AI detection systems successfully. Undetectable AI boasts a 99%+ human pass rate [21]. Writesonic’s Article Writer creates text that varies sentence length and flows naturally [22]. These tools study millions of human-written samples to spot language patterns and turn AI text into writing that sounds human [23]. A 2024 peer-reviewed study revealed something interesting – Undetectable AI scored 100% accuracy in spotting AI-generated content without any false positives for human writing [21].
Improving AI Detectors: Can They Keep Up?
Most AI detectors achieve only 60-70% accuracy [4]. They often label text as human-written even when it’s not. OpenAI pulled their AI detection software off the market because it didn’t work well enough [5]. Detection tools have a hard time with AI content that someone has lightly edited. Experts call this ongoing advancement of both detection and generation tools an “arms race” [24].
Should We Rely on Detection or Redesign Assignments?
Teachers now prefer changing assignments rather than relying on detection. Good strategies include classroom activities, step-by-step assignments, and content specific to class discussions [25]. A legal expert puts it well: “Probably the best way to guard against inappropriate use of AI-generated text is to redesign your assignments” [25].
Skyline’s academic resources offer updates about AI detection technology and best practices.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Criteria | AI Detectors | Human Judgment | Skyline Academic |
|---|---|---|---|
| False Positive Rate | Up to 50% (Turnitin) | 5% (Teachers) | 0.2% |
| Detection Accuracy | 85-95% (Best solutions) | 57-64% (Average reviewers) | Not mentioned |
| Professional Accuracy | Originality.ai: 100% | 96-100% (Professional reviewers) | Not mentioned |
| Processing Speed | Thousands of documents in seconds | ~5.45 minutes per article | Not mentioned |
| ESL Student Accuracy | 61.2% false flag rate | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Detection Method | Analyzes patterns of perplexity and burstiness | Looks at tone, flow, factual consistency | Advanced pattern analysis of 20,000+ papers |
| Key Strengths | – Quick and flexible – Consistent analysis – Handles large volumes |
– Cultural sensitivity – Ethical reasoning – Understands context |
– Lowest false positive rate – Large training dataset – Leading accuracy in the field |
| Key Limitations | – High false positive rates – Can be bypassed – Misses context |
– Slow processing – Results vary – Limited scaling |
Not mentioned |
Conclusion
AI detection tools and human judgment show a complex digital world that deeply affects academia. Many companies make bold claims, but their AI detectors don’t deal very well with false positive rates. These tools often mistake human work for AI-generated content. ESL and neurodivergent students face the worst impact from these errors, which raises serious ethical questions.
The numbers tell us an interesting story. Most detection tools achieve 60-70% accuracy. Skyline Academic stands out from the crowd with a remarkable 0.2% false positive rate. Their analysis of over 20,000 human-written papers proves why educators should think about which detection methods deserve their trust.
AI detectors’ technical limits come from their dependence on text patterns like perplexity and burstiness. These tools work quickly and consistently but lack human’s intuitive understanding of context. Detection becomes harder as specialized evasion tools get better every day.
More educators now prefer to redesign assignments rather than focus on detection. A balanced approach has emerged as the best solution. Skyline Academic’s tools help with the first screening, while human oversight handles any flagged content. This method protects student’s dignity and addresses valid concerns about AI-generated work.
Without doubt, technology will keep advancing on both sides of this arms race. Detection accuracy will improve, but evasion methods will become more sophisticated. Through this progress, Skyline Academic leads the way with the industry’s best accuracy rates and complete resources to handle these complex challenges.
FAQs
Q1. How accurate are AI detectors in 2025?
AI detectors have improved but are not 100% accurate. Even the best detectors can produce false positives and negatives. Accuracy rates vary widely, with some tools claiming up to 95% accuracy, while others struggle with high error rates.
Q2. Which AI detection tool is considered the most reliable?
While various tools claim high accuracy, Skyline Academic has demonstrated impressive results with a false positive rate of just 0.2% after analyzing over 20,000 human-written papers. However, no single tool is universally considered the most reliable across all scenarios.
Q3. Can Turnitin effectively detect AI-generated content in 2025?
Turnitin has updated its AI writing detection capabilities to include AI bypasser detection. However, studies have shown mixed results, with some reporting high false positive rates. Its effectiveness may vary depending on the specific content and context.
Q4. How do AI detectors compare to human judgment in identifying AI-generated text?
AI detectors can process large volumes of text quickly, but lack human intuition and contextual understanding. Human reviewers, especially professionals, can achieve high accuracy rates but are slower and less scalable. A hybrid approach combining both methods is often recommended for optimal results.
Q5. What are the ethical implications of using AI detectors in academic settings?
The use of AI detectors in academia raises concerns about student trust, potential bias against ESL and neurodivergent students, and the risk of false accusations. These tools can create a low-trust environment and may have serious consequences for students if misused or misinterpreted.